
ASIA-PACIFIC’S LEADING RENEWABLE ENERGY COMPANY
Headquartered in Singapore, Vena Energy is a leading renewable energy company in the Asia Pacific region. We own, develop, construct, operate, manage, and commercialise renewable energy projects in the Asia Pacific region, with an extensive local presence of over 692 employees across 67 corporate and site offices in Japan, North Asia & Australia, Southeast Asia, and India. Our current portfolio includes our core business of solar, onshore wind, and their respective extensions, offshore wind, and energy storage projects.
SOLAR AND Onshore WIND

The Core business of Vena Energy comprises of solar photovoltaics (PV), onshore wind, and their respective extensions such as hybrid systems and floating solar PV.
Since investing in our first development assets in Thailand in 2012, the Core business has expanded significantly with Vena Energy currently operating 70 projects totaling 2.2 GW of gross capacity across seven jurisdictions, and another 1.1 GW under construction, including our first hybrid project.
Offshore wind
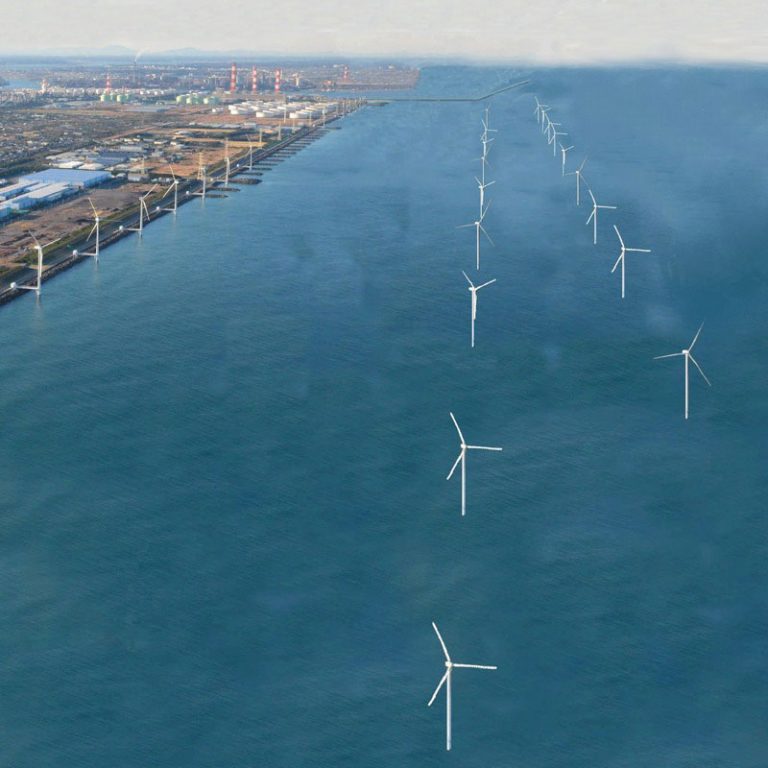

Offshore wind energy is generated via wind farms that are constructed in bodies of water, usually in open sea and coastal areas. Offshore wind farms have better potential for stronger and more stable power generation, mainly attributed to faster and more predictable wind flows over oceans, in addition to the absence of terrain effects.
Today, Vena Energy is developing over 4 GW of offshore wind project in key markets such as Japan, North Asia, Australia, and Southeast Asia.
Energy Storage
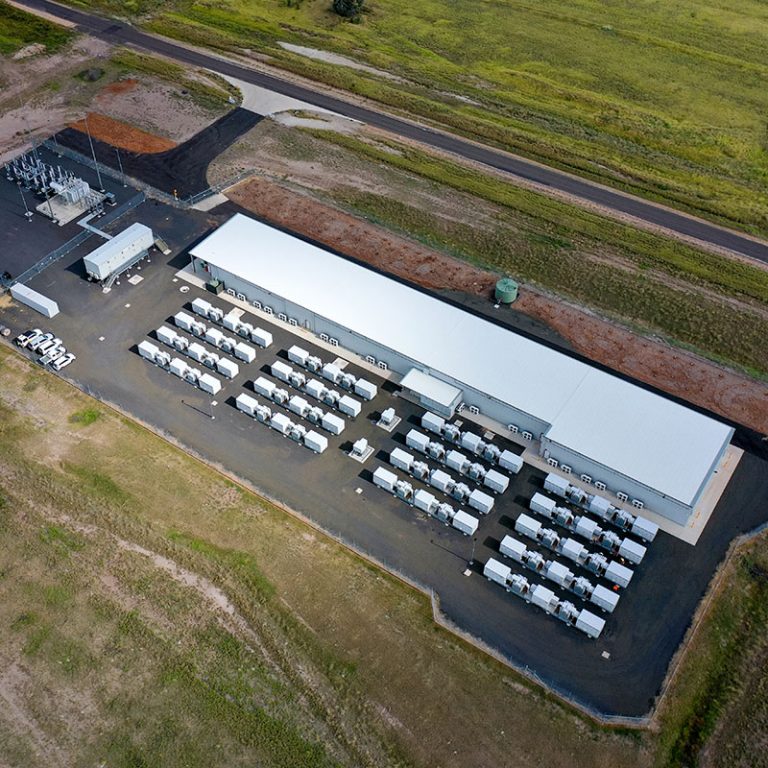

Energy storage solutions allow clean energy to be stored during times of low demand and dispatched at times of low production and peak demand, therefore offering an effective solution to the intermittency of renewable energy. Energy storage represents the next evolution of the energy transition by enabling renewable energy to replace conventional thermal generation as a baseload power source.
Vena Energy has been an early mover in the energy storage sector and is currently constructing two battery energy storage systems totaling 141 MW in Australia and is presently progressing our green hydrogen strategy across the Asia-Pacific region.
VENA ENERGY BY THE NUMBERS
Total capacity2 in wind, solar and battery assets across Asia-Pacific
Solar, wind and battery energy storage projects pipeline
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT METRICS IN 2021
Powered3

in Megalitres5


Notes
- As of December 2021, our operational capacity stands at 2.2 GW and the energy generation arising from those assets was 3.1 TWh.
- Megawatts (MWs) indicate Gross Capacity of all Operational, Construction, Contracted, and Development assets as of December 2021.
- Households Powered is based on annual household electricity consumption of each operating country derived from Residential Electricity Consumption data obtained from the International Energy Agency (2019) and number of households data derived from population data from United Nations (2020) and household size data taken from United Nations (2019) and Statista database (2020).
- Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions Reduction is calculated assuming that the generation from renewable energy plants replaces an equal quantity of electricity generated using coal, gas and oil. Unique GHG emissions factors were calculated for each country based on respective country energy mix and emissions data obtained from BloombergNEF (2019).
- Water Saved is calculated based on the water consumption of solar and wind power plants compared against the various sources of power generation in each country where Vena Energy operates in. Unique water savings factors were calculated for each country based on respective country energy mix obtained from BloombergNEF (2019) and water use intensity factors from a paper titled “Water Demand Scenarios for Electricity Generation at the Global and Regional Levels” by Terrapon-Pfaff, et al., (2020)
- Equivalent Cars Removed from the Road is based on annual GHG emissions of passenger vehicles obtained from the United States Environmental Protection Agency, last updated: March 2022.
- Equivalent Trees Planted is based on the amount of GHG sequestered by a medium growth coniferous or deciduous tree, planted in an urban setting and allowed to grow for 10 years, data obtained from the United States Environmental Protection Agency website, last updated: March 2022.

